how flower colours cater to the taste of pollinating insects
- Written by Jair Garcia, Research fellow, RMIT University
We all know the birds and the bees are important for pollination, and we often notice them in gardens and parks. But what about flies?
Flies are the second most common type of pollinator, so perhaps we should all be taught about the bees, the flies and then the birds. While we know animals may see colour differently, little was known about how fly pollination shapes the types of flowers we can find in nature.
In our new study we address this gap in our knowledge by evaluating how important fly pollinators sense and use colour, and how fly pollinated flowers have evolved colour signals.
 Specialed flower visiting flies: a hoverfly (Eristalis tenax) (left panel), and a bee-fly (Poecilanthrax apache) (right panel)
Michael Becker, Pdeley
Specialed flower visiting flies: a hoverfly (Eristalis tenax) (left panel), and a bee-fly (Poecilanthrax apache) (right panel)
Michael Becker, Pdeley
The way we see influences what we choose
We know that different humans often have preferences for certain colours, and in a similar way bees prefer blue hues.
Our colleague Lea Hannah has observed that hoverflies (Eristalis tenax) are much better at distinguishing between different shades of yellow than between different blues. Other research has also reported hoverflies have innate responses to yellow colours.
Read more: The mystery of the blue flower: nature's rare colour owes its existence to bee vision
Many flowering plants depend on attracting pollinators to reproduce, so the appearance of their flowers has evolved to cater to the preferences of the pollinators. We wanted to find out what this might mean for how different insects like bees or flies shape flower colours in a complex natural environment where both types of insect are present.
The Australian case study
Australia is a natural laboratory for understanding flower evolution due to its geological isolation. On the mainland Australian continent, flowers have predominately evolved colours to suit animal pollination.
Around Australia there are plant communities with different pollinators. For example, Macquarie Island has no bees, and flies are the only animal pollinator.
We assembled data from different locations, including a native habitat in mainland Australia where both bees and flies forage, to model how different insects influence flower colour signal evolution.
Measuring flower colours
Since we know different animals sense colour in different ways, we recorded the spectrum of different wavelengths of light reflected from the flowers with a spectrometer. We subsequently modelled these spectral signatures of plant flowers considering animal perception, allowing us to objectively quantify how signals have evolved. These analyses included mapping the evolutionary ancestry of the plants.
Generalisation or specialisation?
According to one school of thought, flower evolution is driven by competition between flowering plants. In this scenario, different species might have very different colours from one another, to increase their chances of being reliably identified and pollinated. This is a bit like how exclusive brands seek customers by having readily identifiable branding.
An alternative hypothesis to competition is facilitation. Plants may share preferred colour signals to attract a higher number of specific insects. This explanation is like how some competing businesses can do better by being physically close together to attract many customers.
Read more: Plants use advertising-like strategies to attract bees with colour and scent
Our results demonstrate how flower colour signalling has dynamically evolved depending on the availability of insect pollinators, as happens in marketplaces.
In Victoria, flowers have converged to evolve colour signals preferred by their pollinators. The flowers of fly-pollinated orchids are typically yellowish-green, while closely related orchids pollinated by bees have more bluish and purple colours. The flowers appeared to share the preferred colours of their main pollinator, consistent with a facilitation hypothesis.
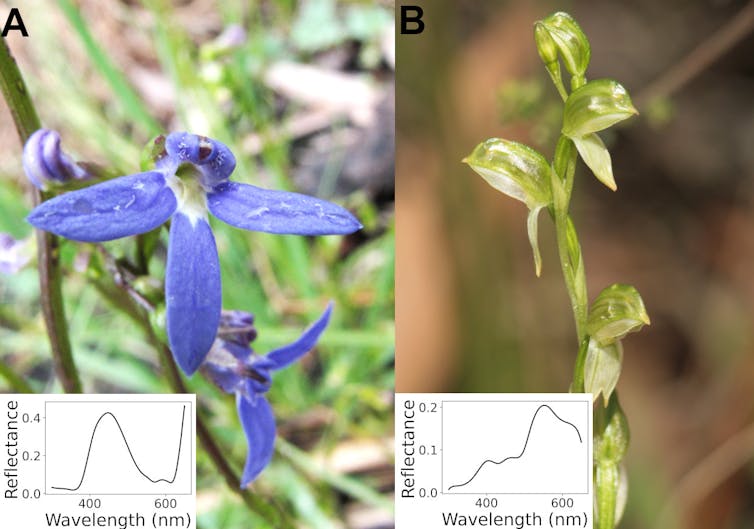 Typical flowers preferred by bees (Lobelia rhombifolia, left panel) and flies (Pterostylis melagramma, right panel) encountered in our study sites. Inserts show the spectral profile for each species as measured by a spectrometer.
Mani Shrestha
Typical flowers preferred by bees (Lobelia rhombifolia, left panel) and flies (Pterostylis melagramma, right panel) encountered in our study sites. Inserts show the spectral profile for each species as measured by a spectrometer.
Mani Shrestha
Our research showed flies can see differences between flowers of different species in response to the pollinator local “market”.
On Macquarie Island, where flies are the only pollinators, flower colours diverge from each other – but still stay within the range of the flies’ preferred colours. This is consistent with a competition strategy, where differences between plant species allow flies to more easily identify the colour of recently visited flowers.
When both fly and bee pollinators are present, flowers pollinated by flies appear to “filter out” bees to reduce the number of ineffective and opportunistic visitors. For example, in the Himalayas specialised plants require flies with long tongues to access floral rewards. This is similar to when a store wants to exclusively attract customers specifically interested in their product range.
Our findings on fly colour vision, along with novel precision agriculture techniques, can help using flies as alternative pollinators of crops. It also allows us to understand that if we want to see a full range of pollinating insects including beautiful hoverflies in our parks and gardens, we need to plant a range of flower types and colours.
Authors: Jair Garcia, Research fellow, RMIT University





